STUDENT RESOURCES
Tools and Class Materials
Power Point Presentations (PDF)
CLASS A -
CLASS B -
CLASS C -
Glossary - Class A
-
Aesthetic - concerned with beauty or the appreciation of beauty. Taste.
-
Arrangement - an arrangement is a musical adaptation of an existing composition.
-
Atonal - not written in any key or mode
-
Avant-garde - new and unusual or experimental ideas, especially in the arts, or the people introducing them
-
Cadence - a sequence of notes or chords comprising the close of a musical phrase
-
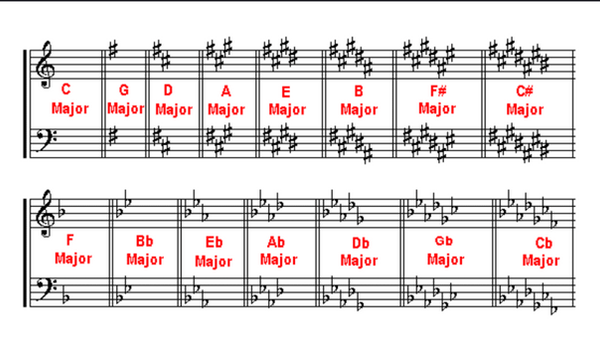
Circle of Fifths - a way of organizing the 12 chromatic pitches as a sequence of perfect fifths
-
Chord - three or more single pitches heard simultaneously
-
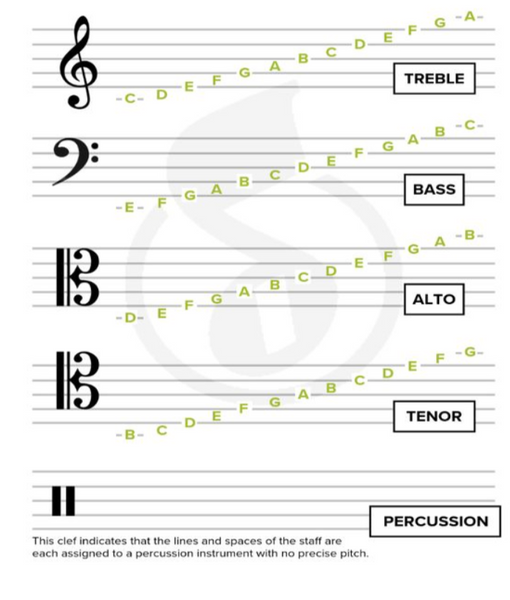
Clef - a sign placed on the staff in writing music to show what pitch is represented by each line and space
-
Contour - the shape and direction of melodic lines or lines of music in a song
-
Diatonic - involving only notes proper to the prevailing key without chromatic alteration.
-
Diction -the pronunciation or enunciation of your vocal expression
-
Dissonant - lacking harmony
-
Groove - In music, groove is the sense of an effect ("feel") of changing pattern in a propulsive rhythm or sense of "swing"
-
Harmony - the sound of two or more notes heard simultaneously
-
Instrumentation - the art of combining instruments based on their capabilities of producing various timbres or colors in any sort of musical composition
-
Interval -an interval is a difference in pitch between two sounds
-
Jargon - special words or expressions that are used by a particular profession or group and are difficult for others to understand
-
Key Signature - any of several combinations of sharps or flats after the clef at the beginning of each stave, indicating the key of a composition
-
Melody - the aesthetic product of a given succession of pitches in musical time, implying rhythmically ordered movement from pitch to pitch
-
Meter - refers to regularly recurring patterns and accent such as bars and beats
-
Music - vocal or instrumental sounds (or both) combined in such a way as to produce beauty of form, harmony, and expression of emotion
-
Music Theory - the study of the practices and possibilities of music. Rudiments that are needed to understand music notation.
-
Narrative - music which tells a story
-
Note - the representation of a musical sound
-
Rhythm - the systematic arrangement of musical sounds, principally according to duration and periodic stress
-
Scale - a scale is any set of musical notes ordered by fundamental frequency or pitch.
-
Staff - the foundation upon which notes are drawn
-
Syntax - Analyzing key structure in context of musical syntax means to examine the relationship between keys in a piece of music; Syntax in general can be referred to as a study of the principles and rules needed for the construction of a language or as a term in particular describing these principles and rules for a special language
-
Tendency Chord - the tendency to move to tones of the tonic chord
-
Tendency Note - a tone that is harmonically or melodically unstable and tends naturally to resolve itself either upward or downward
-
Tonal - written in a particular key or chord
-
Variation - a formal technique where material is repeated in an altered form
Glossary - Class B
-
Accent: In music, an accent refers to the emphasis or stress placed on a particular note or
musical element. It can be achieved by playing a note louder or with more emphasis than the
surrounding notes.
● Beat: a regular repeating pulse that underlies a musical pattern.
● Beat Divisions: Beat divisions are subdivisions of the basic beat, often used to create
rhythmic complexity within a piece of music. Common divisions include half notes, quarter
notes, and eighth notes.
● Beats Per Minute (BPM): BPM is a measure of tempo in music and indicates the number of
beats that occur in one minute. It is used to define the speed or pace of a musical piece.
● Chromatic: Chromatic refers to a musical scale or passage that includes all twelve
semitones of the Western musical system. It includes both the natural notes (A, B, C, D, E, F,
G) and their sharps or flats (e.g., A#, C#, D#).
● Circle of Fifths: The circle of fifths is a visual representation of the relationships between the
12 major and minor keys in music. It shows how key signatures are related and helps
musicians understand key changes and chord progressions.
● Downbeat: The downbeat is the first beat of a musical measure, typically the strongest beat,
and serves as a reference point for rhythmic timing in a piece of music.
● Frequency (Music Definition): In music, frequency refers to the rate at which a sound wave
vibrates and produces a musical pitch. It is measured in Hertz (Hz) and determines the pitch
of a note.
● Flat: A flat symbol (♭) in music indicates that a note should be lowered by one semitone. For
example, a B flat (B♭) is one half-step lower than a B natural (B).
● Half Step: A half step is the smallest interval in Western music. It represents the distance
between two adjacent notes on the musical scale.
● Harmony: The sound of two or more notes heard simultaneously.
● Ionian: Ionian is a musical mode and the basis for the major scale.
● Interval: An interval is the distance between two musical notes. It is typically measured in
terms of the number of half steps or semitones between the notes and is crucial for
understanding melody and harmony.
● Jargon: Jargon in music refers to specialized or technical language and terminology used by
musicians and music professionals. It can include terms specific to certain instruments,
genres, or musical theory. -
Pitch: the quality of a sound governed by the rate of vibrations producing it (frequency).
● Measure: A defined segment of time within a piece of music.
● Melody: Melody is a sequence of single notes that are organized in a musically satisfying
fashion, and consisting of different pitches.
● Meter: Meter refers to the organization of beats into regular groupings or patterns. It is
indicated by a time signature at the beginning of a piece and helps define the rhythmic
structure of the music.
● Mode: A mode is a musical scale variation that is derived from a parent scale
● Natural: In music, "natural" refers to a note that is not altered by a sharp or flat symbol.
● Note: A note is a fundamental element of music, representing a specific pitch or musical
sound.
● Octave: The distance between one note (like C#) and the next note bearing its same name
(the next C# that's either higher or lower). In terms of physics, an octave is the distance
between one note and another note that's double its frequency.
● Pentatonic: A pentatonic scale is a five-note scale that is commonly used in various musical
traditions.
● Percussion: Percussion refers to a family of musical instruments that are sounded by
striking or shaking. These instruments include drums, cymbals, xylophones, and more.
● Rhythm: The systematic arrangement of musical sounds, principally according to duration
and periodic stress.
● Scale: A scale is any set of musical notes ordered by fundamental frequency or pitch
● Sharp: A sharp symbol (♯) in music indicates that a note should be raised by one semitone.
For example, a C sharp (C♯) is one half-step higher than a C natural (C).
● Tempo: Tempo is the speed or pace at which a piece of music is performed. Time signature:
a notation at the beginning of a musical composition that indicates the number of beats in
each measure and the type of note that receives one beat.
● Whole Step: A whole step, also known as a whole tone, is an interval consisting of two half
steps or two semitones. It is a larger distance between two notes on the musical scale.
Notes on a Piano

Notes on a Staff

Circle of Fifths

Scales



Chord Tendencies

Key Signatures
Beat Divisions
